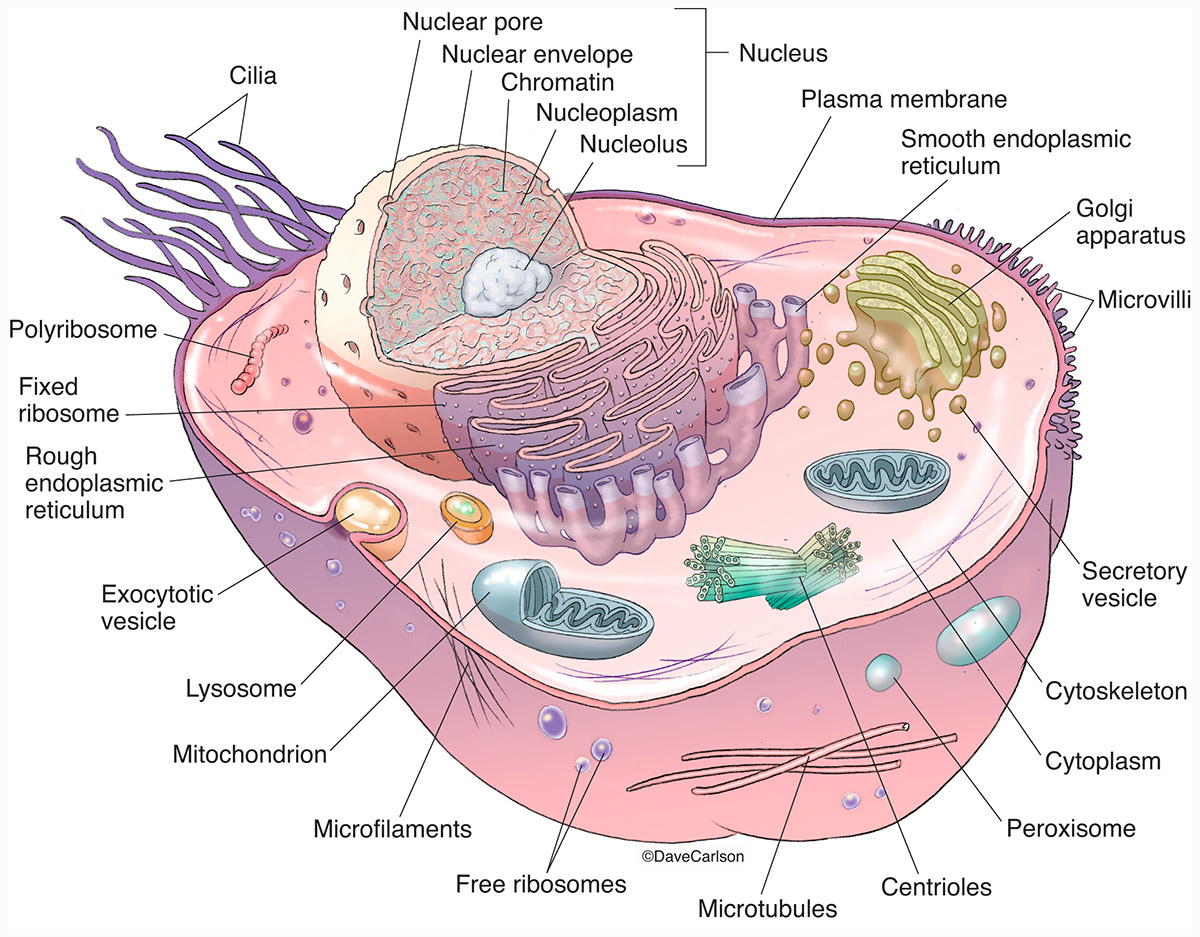
Animal Cell With Structure / Animal Cell Structure And Organelles With Their Functions Jotscroll
Eukaryotic cells also have organelles, which are membrane-bound structures found within the cell. If you looked at eukaryotic cells under a microscope, you'd see distinct structures of all shapes and sizes. Prokaryotic cells, on the other hand, would look more uniform because they don't have those membrane-bound structures to break up the cell.

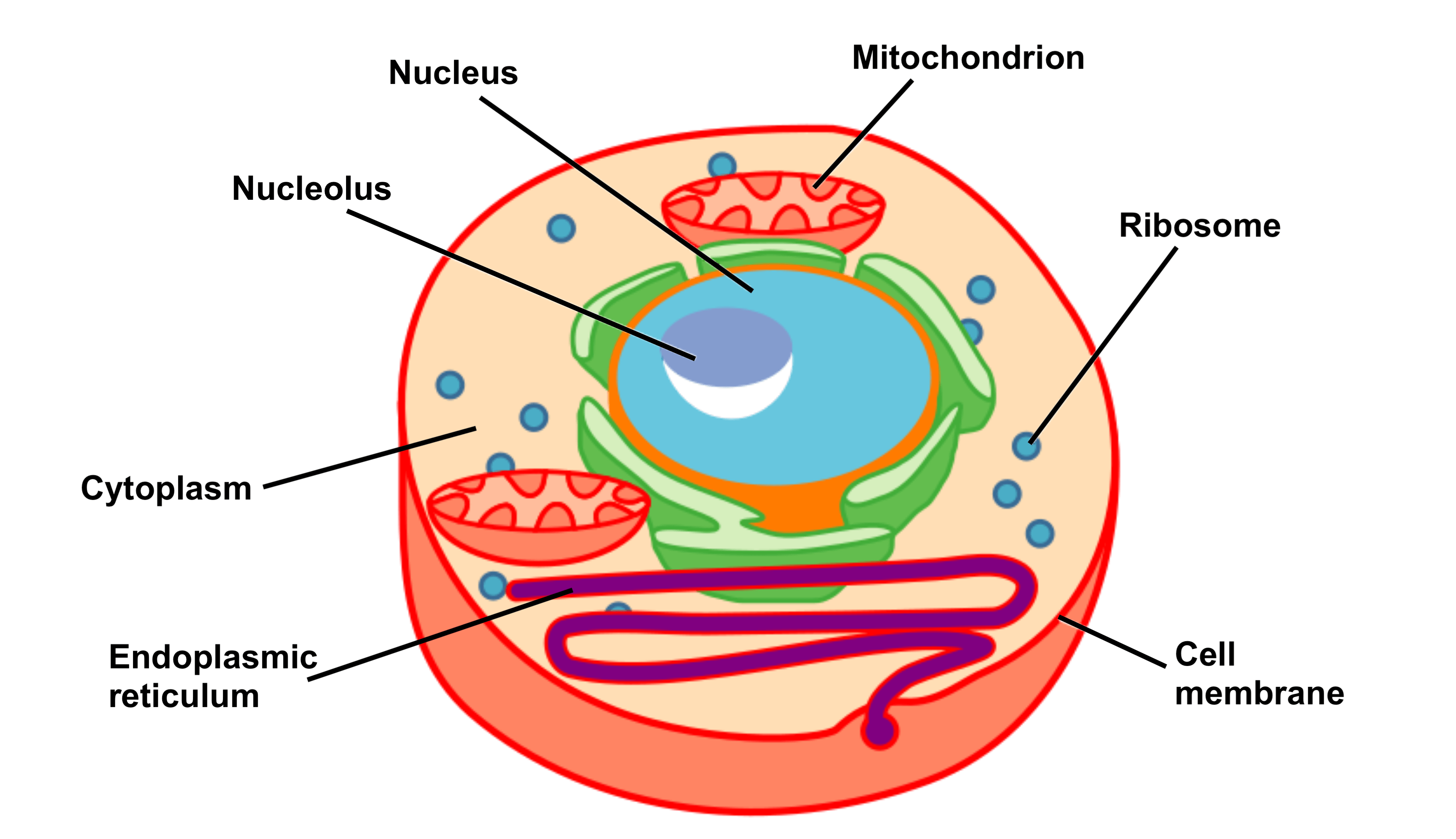
Figure 1.1. Eukaryotic Cell Numerous membranebound organelles are found in the cytoplasm of a
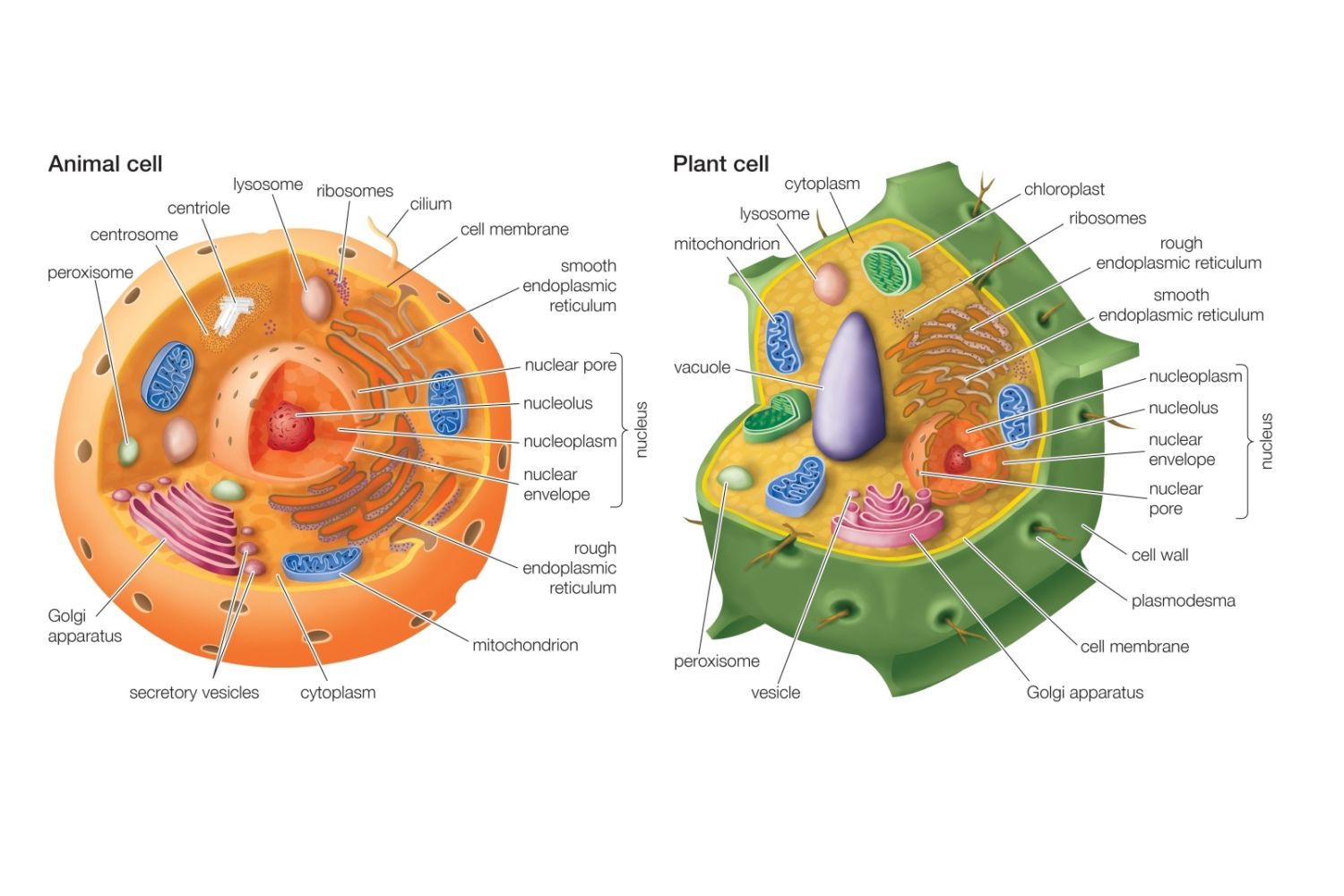
Labeled diagram of a typical animal cell Nucleus. The nucleus contains all the genetic material in a cell. This genetic information is called deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA). DNA contains all the instructions for making proteins, which control all of the body's activities. Therefore, the nucleus is like the manager's office of the cell.

Cell Structure
Animal cell size and shape. Animal cells come in all kinds of shapes and sizes, with their size ranging from a few millimeters to micrometers. The largest animal cell is the ostrich egg which has a 5-inch diameter, weighing about 1.2-1.4 kg and the smallest animal cells are neurons of about 100 microns in diameter.

Plant Cell Labelled Diagram Ideas of Europedias
Cell diagram labeled. For this exercise we'll start with an image of a cell diagram ready labeled. Study this and make sure that you're clear about which structure is found where. Cell diagram unlabeled. It's time to label the cell yourself! As you fill in the cell structure worksheet, remember the functions of each part of the cell that.
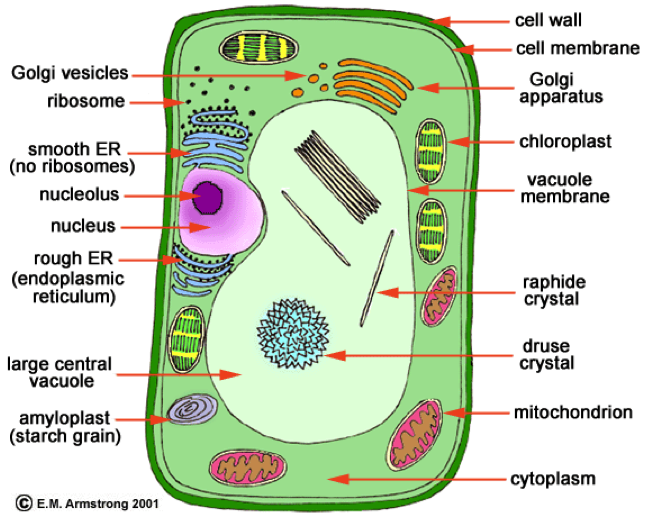
Biology Cell Structure and Functions
Labeled Animal Cell Diagram. Blank Animal Cell Diagram Worksheet. The third and fourth diagrams are animal cell diagram worksheets. Quiz yourself by filling in the blanks. Unlabeled Animal Cell Diagram. Finally, an unlabeled version of the diagram is included at the bottom of the page, in color and black and white. This may be useful as a.

Organelles, cell growth and cytoskeleton Diagram Quizlet
Cell Notation (Cell Diagrams) Recall that standard cell potentials can be calculated from potentials E 0 cell for both oxidation and reduction reactions. A positive cell potential indicates that the reaction proceeds spontaneously in the direction in which the reaction is written. Conversely, a reaction with a negative cell potential proceeds.
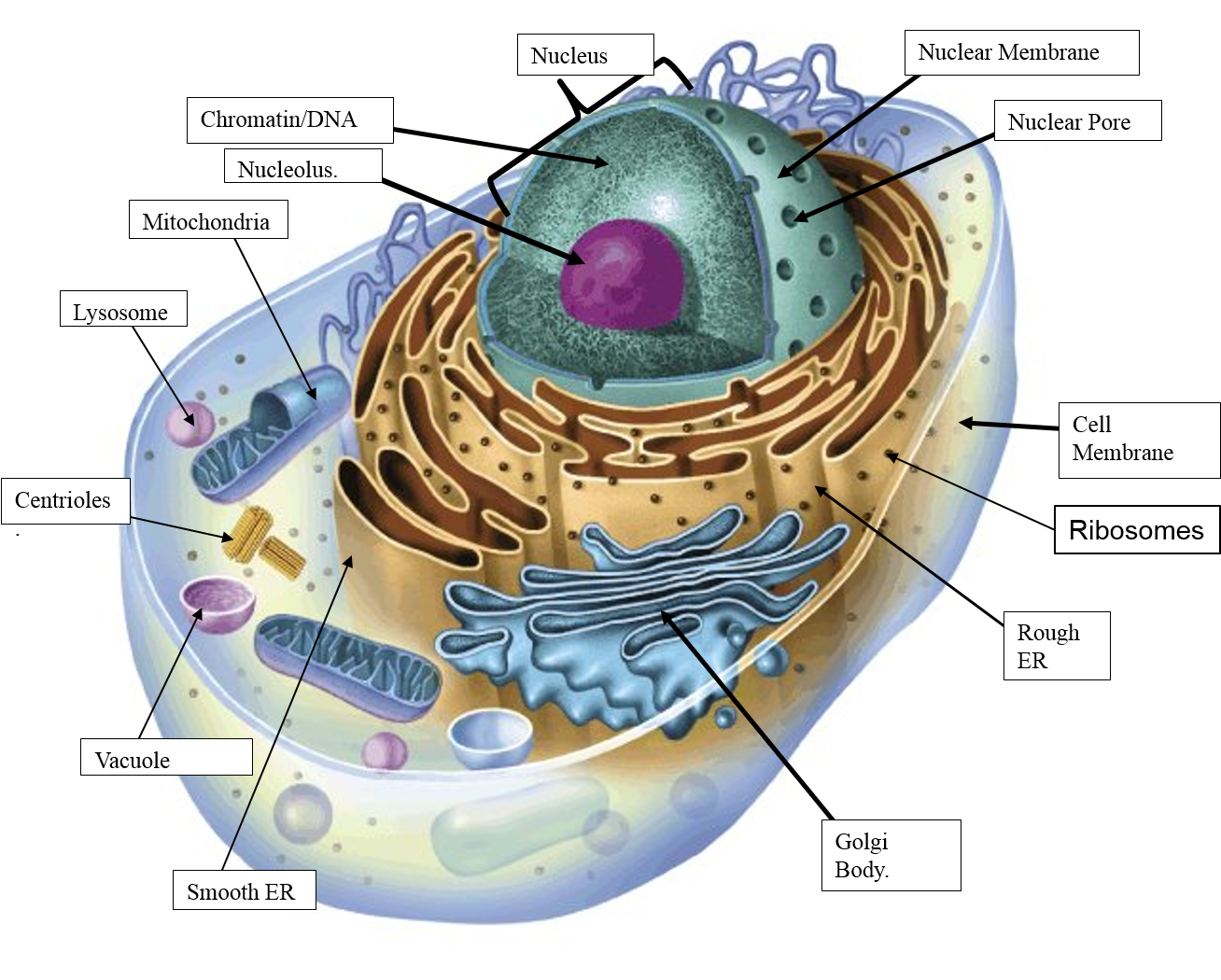
South Pontotoc Biology Plant and Animal Cell Diagrams
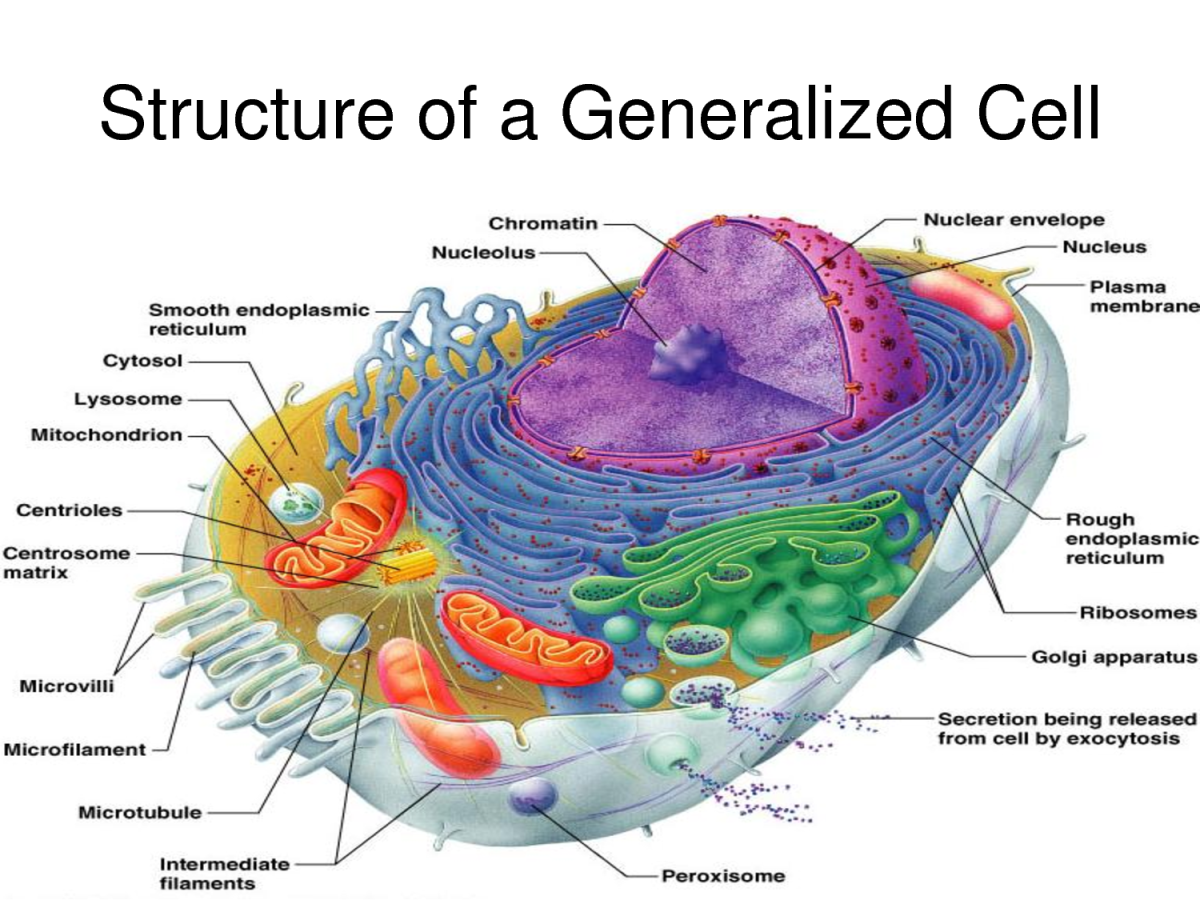
Diagram of a plant cell with components labeled. Image modified from OpenStax Biology. [Attribution and references]. is the transport network of the cell and it extends from and connects the nuclear membrane to the plasma membrane of a cell. But then whenever we draw a diagram of a typical plant or animal cell, we never extend it to the.
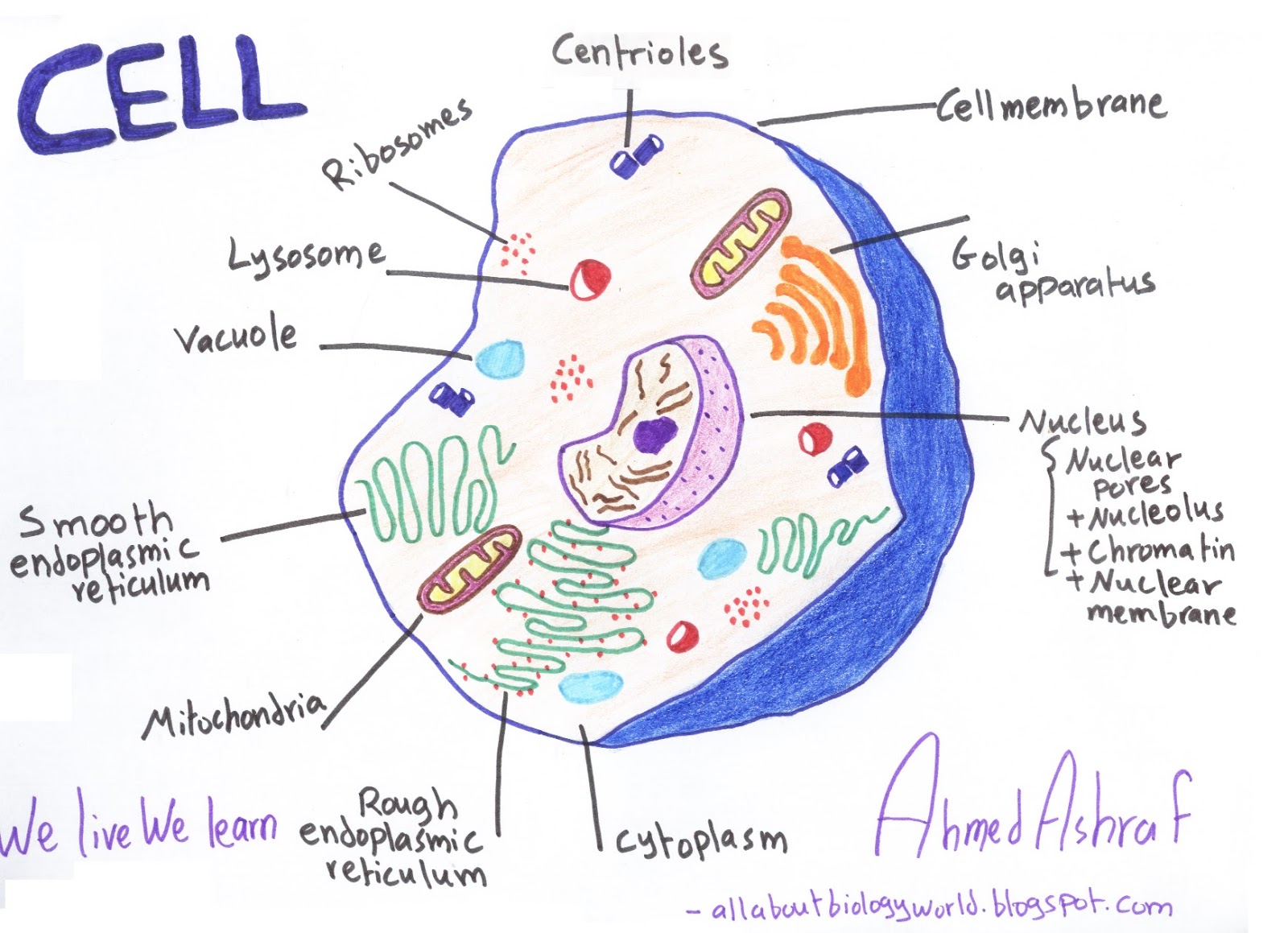
Biology Club Our cells 1 ( structure, function, division, disorder & cycle )
As observed in the labeled animal cell diagram, the cell membrane forms the confining factor of the cell, that is it envelopes the cell constituents together and gives the cell its shape, form, and existence. Cell membrane is made up of lipids and proteins and forms a barrier between the extracellular liquid bathing all cells on the exterior.

Biology 101 Cells Owlcation
The cell structure illustrations for these diagrams were generated in BioRender. Both diagrams feature a drag-and-drop labelling activity created with H5P here on Learnful. These h5p resources are made available openly with the CC BY license. Plant Cell Structure: Animal Cell Structure:

animal cell diagram easy Kris Hammett
Animal cells have a basic structure. Below the basic structure is shown in the same animal cell, on the left viewed with the light microscope, and on the right with the transmission electron.

Explain the nucleus of a cell with a neat labeled diagram Science Cell Structure and
A diagram of a plasma membrane shows a phospholipid bilayer with 3 proteins embedded in the bilayer. One of the proteins is shown with a channel in it. The 3 proteins have lines with the label integral membrane proteins. On the inner side of the phospholipid bilayer is another protein that is positioned up against the inner portion of the bilayer.
Plant And Animal Cell Ks2 BBC GCSE Bitesize Growth / It is easier to describe these parts
Eukaryotic Cells: 1. Eukaryotes are sophisticated cells with a well defined nucleus and cell organelles. 2. The cells are comparatively larger in size (10-100 μm). 3. Unicellular to multicellular in nature and evolved ~1 billion years ago. 4. The cell membrane is semipermeable and flexible. 5. These cells reproduce both asexually and sexually.

The animal cell diagram. Vector illustration on white Etsy in 2021 Animal cell, Cell diagram
An additional non-living layer present outside the cell membrane in some cells that provides structure, protection, and filtering mechanism to the cell is the cell wall. Structure of Cell Wall In a plant cell, the cell wall is made up of cellulose, hemicellulose, and proteins while in a fungal cell, it is composed of chitin.
Cell Structure and Function Part 1 The Organelles Medical Exam Prep
A plasma membrane encloses the cell contents of both plant and animal cells, but it is the outer coating of an animal cell. Animal Cell Structure: Organelles and Their Functions. Worksheet: Label the Parts of an Animal Cell [Google Apps worksheet][worksheet PDF][worksheet PNG][answers PNG] Common Questions About Animal Cells.

What is a cell? Facts
Structure of a cell: Quiz 2; Structure of a cell: Unit test; About this unit. This unit is part of the Biology library. Browse videos, articles, and exercises by topic. Introduction to cells. Start your cellular journey the right way: with some history and some microscopy! Here, we'll learn more about how cells were discovered, how they can be.
Animal Cell Well Labelled Diagram Preview We did not find results for
A cell is the smallest living thing in the human organism, and all living structures in the human body are made of cells. There are hundreds of different types of cells in the human body, which vary in shape (e.g. round, flat, long and thin, short and thick) and size (e.g. small granule cells of the cerebellum in the brain (4 micrometers), up to the huge oocytes (eggs) produced in the female.